Factors affecting liquefaction characteristics
液状化特性に及ぼす諸要因
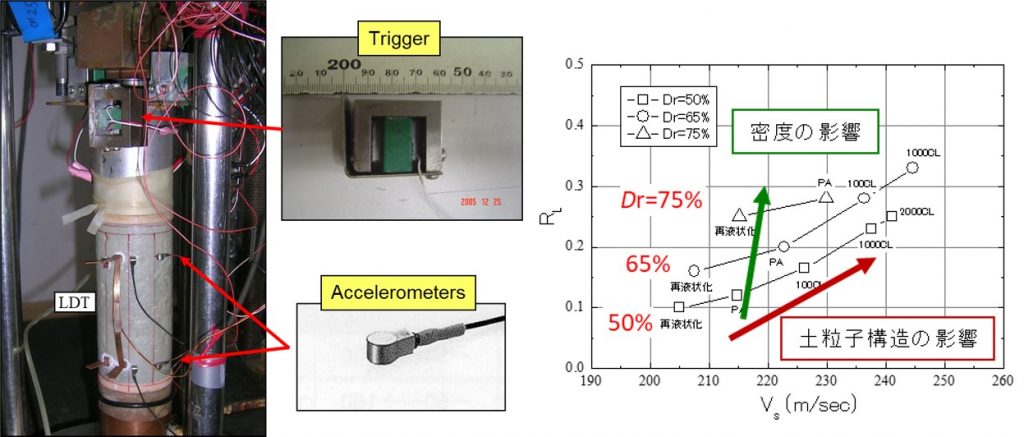
The liquefaction characteristics of a certain soil are greatly affected not only by the soil density, but also by aging effects, pre-shearing by past earthquakes and liquefaction history.
We aim to realize a rational liquefaction assessment by studying the various effects on the liquefaction characteristics using advanced soil testing equipment.
地盤の液状化特性は、それがたとえ同じ土質で同じ密度であったとしても、セメンテーション効果・土粒子構造に代表される年代効果、過去の地震・液状化履歴、過圧密履歴、現在の応力状態など、様々な影響を大きく受けます。
清田研究室では、微小~100%以上の広範なせん断ひずみ領域を対象として、先進的な土質試験装置を駆使して液状化特性に及ぼす様々な影響を紐解いて、高度な液状化アセスメントの実現を目指します。
Liquefaction strength assessment
新しい液状化強度推定手法の開発
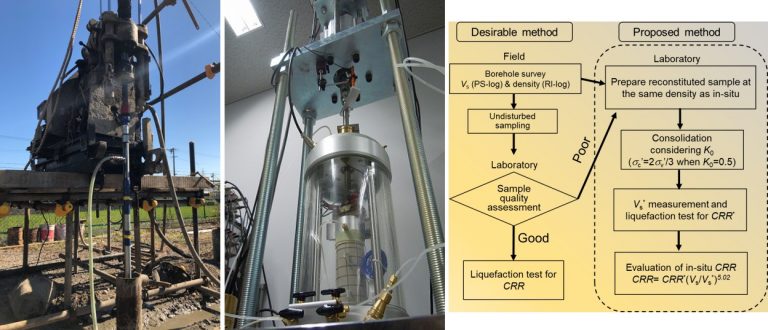
We have proposed a method to evaluate in-situ liquefaction resistance that reflects the effects of soil fabric, previous earthquakes and liquefaction histories as based on the in-situ and laboratory-measured shear wave velocities.
The proposed method can potentially be effectively employed in engineering practice.
従来のN値に基づく液状化判定は過度に安全側の評価となり易く、本来液状化の可能性が低い地盤でも高い危険性が示されることがあります。一方、液状化検討の対象となる緩い砂地盤を、実務レベルで高品質に採取する手法は未だ開発途上であるため、これらの試料を用いた室内試験結果の信頼性は高くないです。
清田研究室では、実務一般で実施される原位置試験と撹乱試料を用いた室内土質試験によって、原地盤(塑性細粒分を含まない沖積~埋立地盤)の年代効果や土粒子構造、過去の地震履歴等の影響が反映された液状化強度を簡易に推定する手法を開発しました。これによって、液状化防災事業への過剰投資が軽減されると共に、投資の適切な分配が成されて、以って地域全体の地震防災能力の向上に繋がることを期待します。
Damage strain of geomaterial and slope stability
地震による地盤損傷と斜面安定
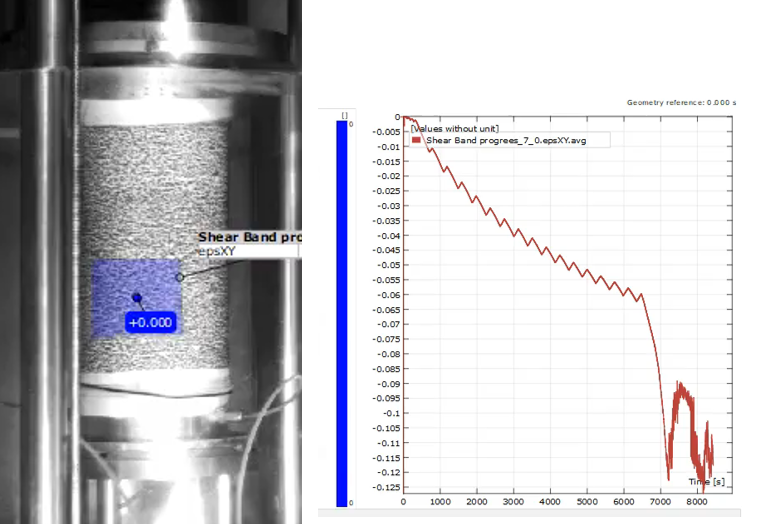
The damage strain accumulated due to the earthquake motion reduces the strength of geomaterial and slope failure may be induced.
We clarify the strength-deformation characteristics of the geomaterial at a large strain level affected by the damage strain using an advanced torsional shear apparatus.
地震動により地盤に蓄積するひずみ(damage strain)によって、地盤の強度は大きく低下して斜面崩壊を誘発することがあります。
本研究では、高さ30cmの供試体に100%以上のせん断ひずみを与えることが可能な特殊な中空ねじり試験装置を用いて、damage strainの影響を受ける大ひずみレベルでの地盤の強度変形特性を明らかにします。
Liquefaction-induced road damage and hazard map
液状化による道路ダメージとハザードマップ構築
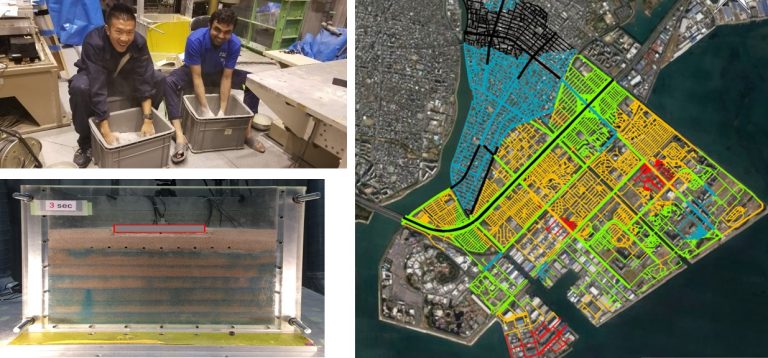
We examine the influence of thickness of road pavement and roadbed on liquefaction-induced road-subsidence through field surveys, airborne LiDAR and shaking table model tests.
A new hazard map is developed that quantitatively shows the expected liquefaction-induced damage to the road-network due to future earthquake.
液状化による道路沈下量に及ぼす道路舗装・路盤層厚の影響を、現場調査・航空LiDAR・振動台模型実験を通じて検討して、地震時の道路網の想定被害を定量的に示す新しいハザードマップを構築します。
Mechanism of long-distance flow-slide
地盤流動メカニズム

We investigate the occurrence mechanism of long-distance flow-slide on very gentle slopes due to the 2018 Sulawesi Earthquake by means of field survey, model test, laboratory soil test, and numerical simulation.
2018年スラウェシ島地震によって、超緩斜面で発生した長距離地盤流動の発生メカニズムを、現場調査、模型実験、室内土質試験、数値解析を駆使して解明します。
